
Hyman Minsky's financial instability hypothesis was a major part of the financial crisis of 2008. But what are his theories, and how did they influence the current global financial crisis? We'll be discussing the Minsky moment, Financial stability, and the Financial instability hypothesis. We will also discuss the implications of this theory on the global economy. After reading this article you will be better equipped to talk with financial advisers about the financial future.
Hyman Minsky
Hyman Minsky was an American economist who lived between 1919 and 1996. He studied at Harvard University and Harvard University. Alvin Hansen was his assistant, who invent the term secular stasis. Minsky taught at Brown, Carnegie-Mellon, and Berekely during his time at Harvard. He was offered a job at Washington University in 1965. Hyman Minsky is best known for his theory of financial instability, which he developed in his book Stabilizing an Unstable Economy.
Financial instability hypothesis
Financial instability hypothesis is a theory that says that if extreme price fluctuations were eliminated, there would be higher growth and less unemployment. Minsky argues that some aspects of the capitalist system can cause extreme price fluctuations. He argues that inflation can be caused by the constant need to bail-out financially distressed institutions. Furthermore, he argues that there is no magical solution to financial instability.
Minsky moment
Minsky moments refer to sudden and dramatic drops in asset values. These events usually mark the end or a boom in a specific market. The severity of the crisis correlates with the period of recent bullish speculation. Many will demand a "new beginning" when this happens. While others will praise the end the economic cycle, some will be critical. The key question in both cases is how to avoid a Minsky moment.
2008 Financial Crisis
Hyman Minsky is a renowned economist who earned his Ph.D. from Harvard. He has taught at Harvard, Berkeley University, and Washington University. He was previously the director of St. Louis' Mark Twain Bank. Minsky developed a model of the credit cycle, which consists of five stages: euphoria, profit taking, panic, and displacement. These stages are triggered when there is an abrupt change in economic policy.
Minsky moment: Economics theory behind
The Minsky Moment was a crucial turning point in 2008's subprime mortgage crisis. Easy access to credit led to household debt accumulation, and asset prices rose. This unsustainable bullish speculation supported the US economy for a long period, but ultimately led to its collapse. The housing market began to slide in 2006 and was subsequently destroyed by the Great Recession in 2008

Minsky cycle has an impact on the global economy
Minsky cycles are a theoretical model that captures changes in financing arrangements. These can lead to an increase in risk taking. Hedge financing is the first phase. This occurs when the expected revenues are sufficient to repay the principal amount. The second phase refers to speculative financial, where lenders use the profits from capital gains to meet their debt obligations.
FAQ
AI: Is it good or evil?
AI is seen both positively and negatively. It allows us to accomplish things more quickly than ever before, which is a positive aspect. It is no longer necessary to spend hours creating programs that do tasks like word processing or spreadsheets. Instead, instead we ask our computers how to do these tasks.
On the other side, many fear that AI could eventually replace humans. Many believe that robots will eventually become smarter than their creators. This means that they may start taking over jobs.
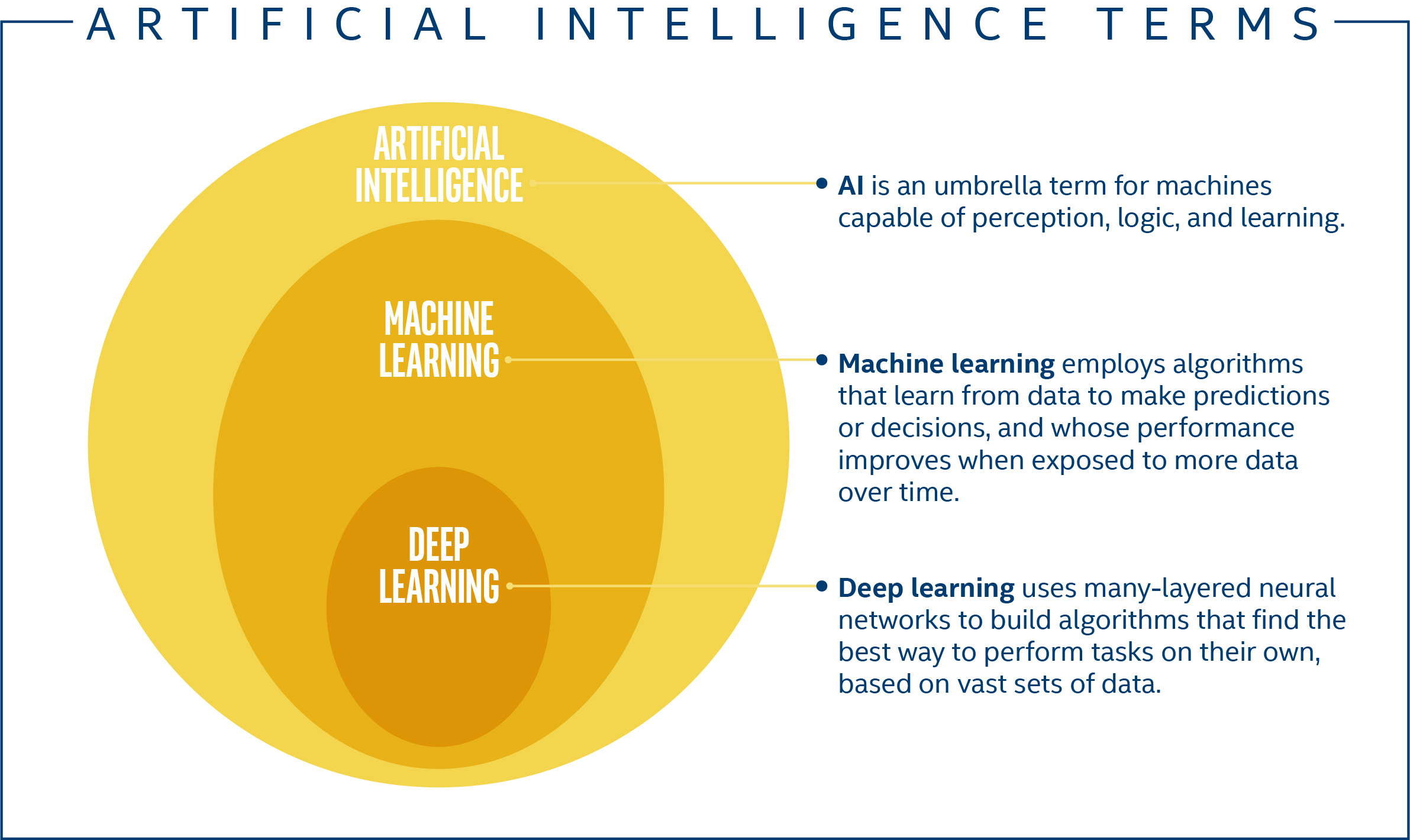
AI is used for what?
Artificial intelligence is an area of computer science that deals with the simulation of intelligent behavior for practical applications such as robotics, natural language processing, game playing, etc.
AI can also be referred to by the term machine learning. This is the study of how machines learn and operate without being explicitly programmed.
AI is often used for the following reasons:
-
To make life easier.
-
To be better than ourselves at doing things.
A good example of this would be self-driving cars. AI can take the place of a driver.
How will governments regulate AI?
AI regulation is something that governments already do, but they need to be better. They should ensure that citizens have control over the use of their data. Companies shouldn't use AI to obstruct their rights.
They also need ensure that we aren’t creating an unfair environment for different types and businesses. Small business owners who want to use AI for their business should be allowed to do this without restrictions from large companies.
What are some examples AI-related applications?
AI is used in many fields, including finance and healthcare, manufacturing, transport, energy, education, law enforcement, defense, and government. Here are just some examples:
-
Finance – AI is already helping banks detect fraud. AI can detect suspicious activity in millions of transactions each day by scanning them.
-
Healthcare – AI is used for diagnosing diseases, spotting cancerous cells, as well as recommending treatments.
-
Manufacturing - AI in factories is used to increase efficiency, and decrease costs.
-
Transportation – Self-driving cars were successfully tested in California. They are currently being tested all over the world.
-
Utilities use AI to monitor patterns of power consumption.
-
Education - AI can be used to teach. For example, students can interact with robots via their smartphones.
-
Government - AI can be used within government to track terrorists, criminals, or missing people.
-
Law Enforcement - AI is used in police investigations. Detectives can search databases containing thousands of hours of CCTV footage.
-
Defense - AI systems can be used offensively as well defensively. Offensively, AI systems can be used to hack into enemy computers. Defensively, AI can be used to protect military bases against cyber attacks.
Statistics
- In the first half of 2017, the company discovered and banned 300,000 terrorist-linked accounts, 95 percent of which were found by non-human, artificially intelligent machines. (builtin.com)
- A 2021 Pew Research survey revealed that 37 percent of respondents who are more concerned than excited about AI had concerns including job loss, privacy, and AI's potential to “surpass human skills.” (builtin.com)
- Additionally, keeping in mind the current crisis, the AI is designed in a manner where it reduces the carbon footprint by 20-40%. (analyticsinsight.net)
- That's as many of us that have been in that AI space would say, it's about 70 or 80 percent of the work. (finra.org)
- The company's AI team trained an image recognition model to 85 percent accuracy using billions of public Instagram photos tagged with hashtags. (builtin.com)
External Links
How To
How do I start using AI?
An algorithm that learns from its errors is one way to use artificial intelligence. The algorithm can then be improved upon by applying this learning.
You could, for example, add a feature that suggests words to complete your sentence if you are writing a text message. It would take information from your previous messages and suggest similar phrases to you.
However, it is necessary to train the system to understand what you are trying to communicate.
You can even create a chatbot to respond to your questions. For example, you might ask, "what time does my flight leave?" The bot will tell you that the next flight leaves at 8 a.m.
Take a look at this guide to learn how to start machine learning.